Flooding in Spain - October 2024
In late October, 2024, torrential rain fell over parts of eastern Spain. These rains resulted in flooding that resulted in the deaths of hundreds of people as streets turned into rivers, and homes and bridges were swept away. Tragically, over 200 people died from the floods and many more were unaccounted for.
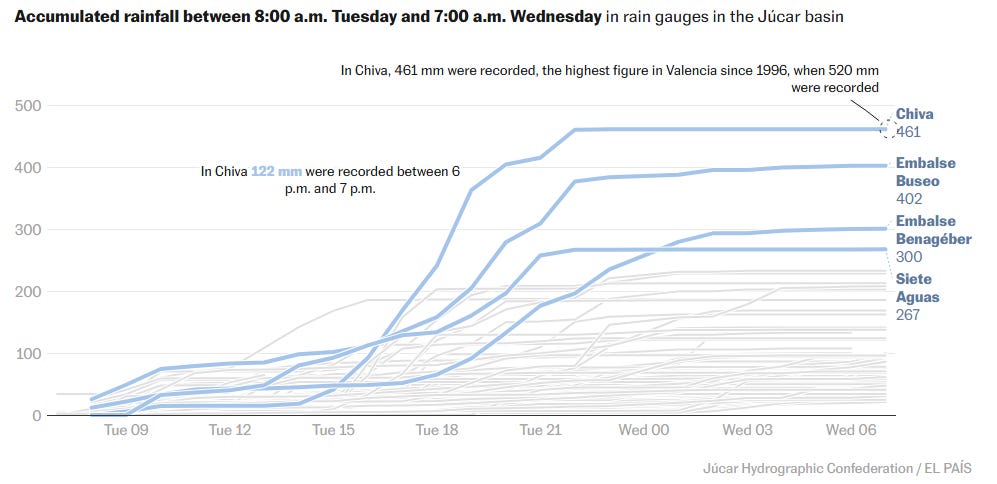
Over a period of eight hours on October 29, as much as 500 litres of water per square metre1 fell over an area near Valencia, Spain. In the map below (reference: A visual guide to understanding the deadly floods in Spain | Climate | EL PAÍS English), each blue dot represents the location of rain measurements over a 24-hour period. The bigger dots show locations of higher rainfall, with the highest iln a place called Chiva, where 460 millimetres of rain fell in 24 hours.
The same website (A visual guide to understanding the deadly floods in Spain | Climate | EL PAÍS English) also shows a series of graphs of the accumulated rainfall over that same 24-hour period. Below, you can see that most of the rain fell in an 8 - 10 hour window ferom about 3 pm to 11 pm on Tuesday, October 29.
I have difficulty imagining what that much rain is like. This past summer, Toronto experience flooding when the city got about 100 mm of rain fell over a 24-hour period. Back in 1954, Hurricane Hazel hit Toronto and between 100 and 200 mm of rain fell in less than a day. But this rainfall event in Spain dropped over 400 mm in 8 hours! According to some reports, that amount (400 to 500 mm) is the total amount of rain that typically falls in that area in one full year!
This part of Eastern and Southern Spain has historically been prone to heavy rainfall events due to the country’s location between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Cold air fronts from the ocean can meet warmer, humid air masses from the sea. This, combined with the high altitudes of the mountains in Spain can lead to favourable conditions for storm events.
In addition, the average sea surface temperature (SST) of the Mediterranean Sea has been rising due to climate change. This increase in temperature of the Mediterranean Sea leads to warmer and more humid temperatures in the atmosphere, which can lead to more frequent and intense storm events.
There are some devastating photos from the flash flooding that occured in Spain last month. There are also documented cases of neighbouring villages gathering to help and clear the debris. Here are some links to some of the photos and videos. The links also include more details about the tragic events:
What caused deadly floods in Spain? The impact of DANA explained | Reuters
Why were the floods in Spain so bad? A visual guide | Spain | The Guardian
A visual guide to understanding the deadly floods in Spain | Climate | EL PAÍS English
Thanks for reading the Water Droplet! Stay tuned for more interesting articles on water. To get email notifications of new articles, sign up here:
In Europe, rainfall is measured in units of litres per square metre. We (in Canada) typically report rainfall in millimetres. So 500 litres/square metre is 0.5 cubic metres per square metre, or 500 millimetres. In southern Ontario, we typically get about 1000 millimetres of rain in a calendar year. Half of that annual average fell in 8 hours in parts of Spain!